About Error Analysis | ||
| ||
The total error is calculated for each response using one of four different approaches (average error, maximum error, root mean square error, R2).
The total error is presented visually for each response using four different graph types:
-
Actual versus predicted fit
-
Residual scatter
-
Residual frequency
-
Total Error bar chart
The error is calculated based on a number of sample points specifically allocated for error analysis. These points are defined when you create the approximation (see Creating Approximations).
You use the Design Gateway’s Approximation Error Analysis dialog box or the Runtime Gateway’s Error Analysis subtab to view the approximation errors. Isight displays the following information:
-
A table of error values for each output parameter, with a list of error types, and a text box for setting the acceptable level of error for the error type. Outputs with errors exceeding the acceptable level are highlighted in red.
-
A tabbed notebook panel with a graphical representation of error information for one or more output parameters (responses).
The figure below shows an example of the Design Gateway’s Approximation Error Analysis dialog box:
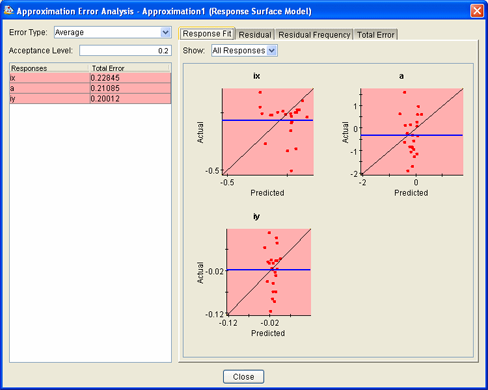
Note: Changing the selected error type or acceptance level on the left side of the dialog box does not change the information displayed on the right side of the dialog box.